About
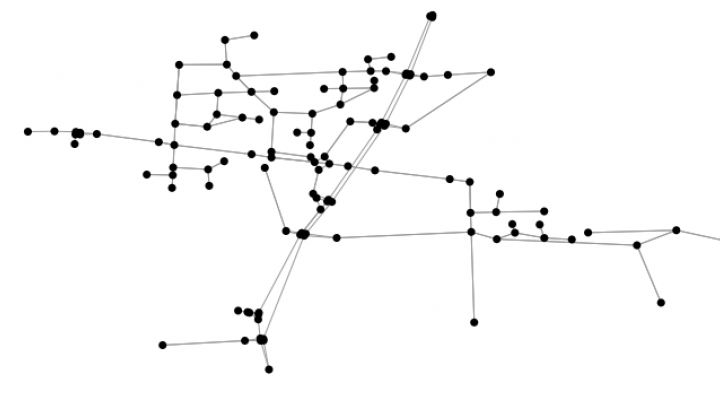
Strengthening public transport is an essential contribution to the mobility turnaround.
Digitization enables a better understanding between supply and demand.

Related Research Projects
Related Transfer Projects
Related Publications
Published
Avermann, N., & Schlüter, J. C. (2019). Determinants of customer satisfaction with a true door-to-door DRT service in rural Germany. Research in Transportation Business & Management, 32: 100420. doi:10.1016/j.rtbm.2019.100420
Gebauer, A., Fingerhut, J., Lahner, J., & Schlüter, J. C. (2019). Verkehrsanbindung von Berufsschülern. Standort, 43(1), 9-19.
doi:10.1007/s00548-019-00567-4
Grunicke, C., Schlüter, J. C., & Jokinen, J.-P. (2020). Evaluation methods and governance practices of new flexible passenger transport projects. Research in Transportation Business & Management, 100575. doi:10.1016/j.rtbm.2020.100575
Harbering, M., & Schlüter, J. C. (2020). Determinants of transport mode choice in metropolitan areas the case of the metropolitan area of the Valley of Mexico. Journal of Transport Geography, 87: 102766. doi:10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2020.102766
Kersting, M., Matthies, E., Lahner, J., & Schlüter, J. (2020). A socioeconomic analysis of commuting professionals. Transportation, 1-32.
doi:10.1007/s11116-020-10124-w
Lahner, J., Schlüter, J. C., & Sörensen, L. (2019). Digitalisierung im ÖPNV: vom Rufbus zu einem intelligenten nachfrageorientierten System im ländlichen Raum. Neues Archiv für Niedersachsen, II/2019, 178-191. doi:10.5771/9783529096112-178
Matthies, E., Preuß, S., Lahner, J., & Schlüter, J. C. (2019). Alternative Bedienformen im ÖPNV. Implikationen für den Planungsprozess. Zeitschrift für Verkehrswissenschaft, 90, 21-47.
www.z-f-v.de
Nyga, A., Minnich, A., & Schlüter, J. C. (2020). The effects of susceptibility, eco-friendliness and dependence on the Consumers’ Willingness to pay for a door-to-door DRT system. Transportation Research Part A, 132, 540-558. doi:10.1016/j.tra.2019.11.030
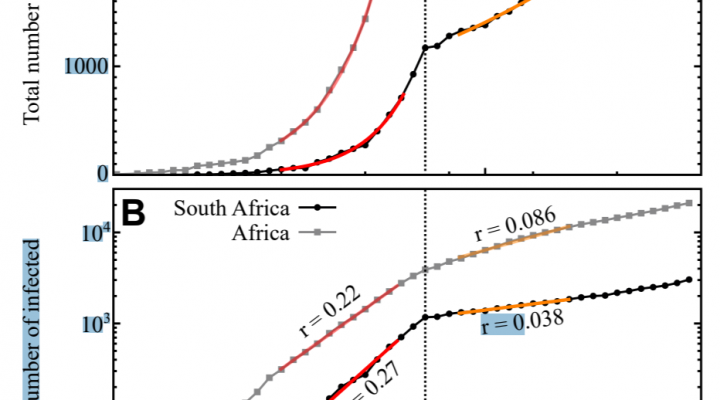
Schlüter, J. C., Frewer, M., Sörensen, L., & Coetzee, J. (2020). A stochastic prediction of minibus taxi driver behaviour in South Africa. Humanities and Social Sciences Communications, 7: 13. doi:10.1057/s41599-020-0508-2
Simons, J., Wacker, B., Bossert, A., & Schlüter, J. C., Verkehrsökonomische Analyse von Minibustaxiverkehren in der Metropolregion Kapstadt und der Minenstadt Rustenburg in Südafrika, Zeitschrift für Verkehrswissenschaft, 91, 1-27.
www.z-f-v.de
Sörensen, L., Bossert, A., Jokinen, J. P., & Schlüter, J. (2020). How much flexibility does rural public transport need?–Implications from a fully flexible DRT system. Transport Policy, 100, 5-20. doi:10.1016/j.tranpol.2020.09.005
In Press
Schlüter, J. C., Simons, J., Sörensen, L., & Coetzee, J. (2021). Optimierung von Minibustaxiverkehren in Südafrika unter Einbindung von Geoinformationssystemen, Standort 45, 96–101.
doi:10.1007/s00548-020-00694-3
Schlüter, J., Bossert, A., Rössy, P., & Kersting, M. (2021). Impact assessment of autonomous demand responsive transport as a link between urban and rural areas. Research in Transportation Business & Management, 39, 100613.
doi:10.1016/j.rtbm.2020.100613
Submitted
Bossert, A., von Hausegger, K., Schlüter, J. C. (06/2020), Behavioural analytics for smart cities: The influence of weather on cycle superhighway utilisation in cities with seasonal inhabitant effects. submitted@Cities
Minnich, A., Herbst, H., Herminghaus, S., Kneib, T., Wacker, B., & Schlüter, J. C. (2024). A behavioral economic perspective on demand responsive transportation. Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives, 27, 101176. doi:10.1016/j.trip.2024.101176
Hesse, H., Kühnel, S., Bossert, A., and Schlüter, J. C., Die Sicherheit des Minibustaxiverkehrs in Südafrika. submitted@Soziale welt
Kersting, M., Kallbach, F., & Schlüter, J. C. (2021). For the young and old alike–An analysis of the determinants of seniors’ satisfaction with the true door-to-door DRT system EcoBus in rural Germany. Journal of Transport Geography, 96, 103173.
doi:10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2021.103173
Knierim, L., & Schlüter, J. C. (2021). The attitude of potentially less mobile people towards demand responsive transport in a rural area in central Germany. Journal of Transport Geography, 96, 103202. doi:10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2021.103202
Minnich, A., Rau, H., Schlüter, J. C. (2020), The effects of financial and non-financial incentives on the usage of adoor-to-door DRT system: Evidence from a field experiment in rural Germany. Center for European, Governance and Economic Development Research (cege) Discussion Papers No. 394
http://hdl.handle.net/10419/218963
Nyga, A., Schlüter, J. C.. How Public is Public Transport? -Does Public Transport Qualify As a Public Good? submitted@Journal of Economic Perspectives
Schöller, G., Sörensen, L. & Schlüter, J. C. (06/2020). Socially-optimal public transport operations in a developing country.
submitted@Transport Policy
Sörensen, L., & Schlüter, J. (2021). How do contract types and incentives influence driver behavior?− An analysis of the Kigali bus network. Humanities and Social Sciences Communications, 8(1), 1-11. doi:10.1057/s41599-021-00896-6
v. Rosenberg, V. H. I., Sörensen, L., & Schlüter, J. C., The Role of the Paratransit Sector in the Public Transport Systems of Latin American Cities
Working Paper
Grunicke, C., Schlüter, J. C., & Jokinen, J. P. (2020). Implementation of a cost-benefit analysis of Demand-Responsive Transport with a Multi-Agent Transport Simulation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2011.12869.
arXiv:2011.12869
Books & Technical Reports
Technischer Bericht Dassel
Technical Report 1: Transportanalyse zur Implementierung eines intelligenten Demand Responsive Transport Systems im ländlichen Raum
Technical Report 2: Transportanalyse zur Implementierung eines intelligenten Demand Responsive Transport Systems im ländlichen Raum
Jokinen, J.-P., Sörensen, L., Schlüter, J. C. (2021), Public transport in low density areas. In: Vickerman, Roger (eds.) International Encyclopedia of Transportation. vol. 1, pp. 589-595. UK: Elsevier Ltd. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-102671-7.10628-1